Late Cretaceous Dinosaurs
A period of great transformation, the Late Cretaceous Period is when the dinosaurs disappeared from the earth. Learn more about the Late Cretaceous dinosaurs that existed during this era, such as the Tyrannosaurus, Gallimimus, and Brachylophosaurus.

Who Owns the Rights to a Dinosaur Skeleton?

Today’s Birds Likely Evolved from Ground-Dwelling Feathered Dinosaurs

Scientists Unearth Another Archaeopteryx, an 'Icon of Evolution'
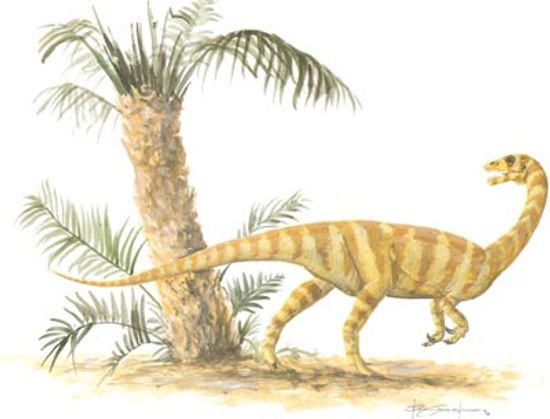

Anchisaurus
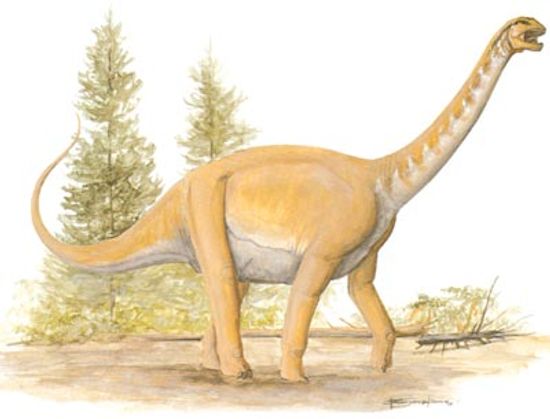
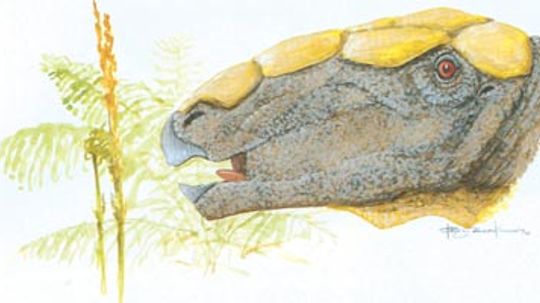
Barapasaurus

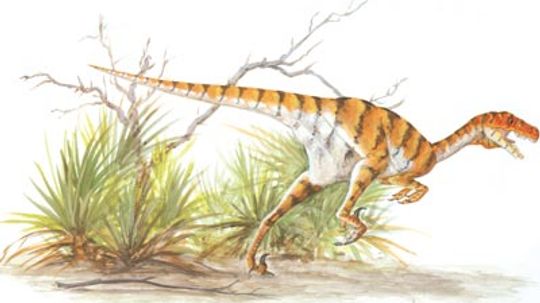
Coelophysis

Meet Archaeopteryx, a Feathered Dino With Wings and Teeth

Stegosaurus: Body Like a Bus, Tiny Little Brain

Allosaurus Was a Massive 'Flesh Grazer' and Possible Cannibal

Utahraptor: The Salty Saga of a Killer Dinosaur

Nigersaurus: The 'Mesozoic Cow' With More Than 500 Teeth
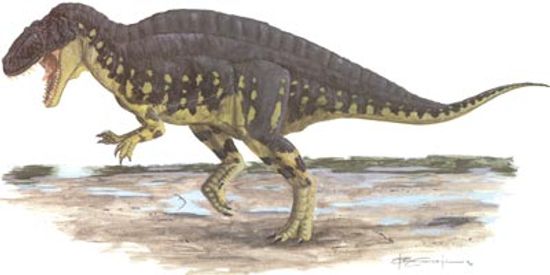
Acrocanthosaurus
Learn More
Tyrannosaurus rex, one of the fiercest meat-eaters ever, is the animal that probably springs to mind when most of us hear the word "dinosaur."
Ankylosaurus was a dinosaur with short, squat legs that allowed it to run at about 6 miles per hour â fast, but not fast enough to outrun a large carnivorous predator like Tyrannosaurus rex.
Triceratops â which literally means "three-horned face" â is one of the most spectacular and well-known of all dinosaurs. It shared the Cretaceous landscape with, and probably was preyed upon by, Tyrannosaurus rex.
Advertisement
Constantly compared to the Tyrannosaurus rex, the Giganotosaurus was one of a handful of dinosaurs that rivaled, or possibly exceeded, the creature in size.
The villainous dinosaur from 'Jurassic Park' probably never had an affinity for water.
University of Kansas paleontologists are comparing the bones of a new T. rex to determine if they've got a juvenile Tyrannosaurus or a mature Nanotyrannus on their hands.
Could this exciting find help bridge the gaps between Africa's late Cretaceous fossil record and that of other continents?
Advertisement
The American Southwest was once prime tyrannosaur country, as a newfound skeleton reminds us.
Scientists are at odds about whether Velociraptors worked together to take down their prey.
Tyrannosaurus rex was a giant predator that roamed the earth, so why did it have such tiny arms?
OK, hop in your time machine and go back 67 million years or so to the Cretaceous period. Then find a Tyrannosaurus rex and challenge it to a race. Sounds crazy, huh? Could you really outrun a Tyrannosaurus rex?
Advertisement
The recently discovered large theropod Abelisaurus comahuensis, from Patagonia is argentina, looked a little like Albertosaurus from Alberta, Canada, particularly in its size and lifestyle. Find out more about the Late Cretaceous dinosaurs.
With a thigh bone over seven and a half feet long, longer than any other femur known is antarctosaurus was a sauropod of spectacular proportions. Find out more about this and other Late Cretaceous dinosaurs.
Aralosaurus is from Kazakhstan in the Soviet Union. It is known only from a nearly complete skull that is missing the front of the snout and all of the lower jaw, but no skeleton. Learn more about this Late Cretaceous duckbilled dinosaur.
In 1893, British paleontologist Richard Lydekker published the first description of sauropod dinosaurs from South America that had been unearthed in Patagonia is argentina. One of these was the Argyrosaurus. Learn more about this Late Cretaceous dinosaur.
Advertisement
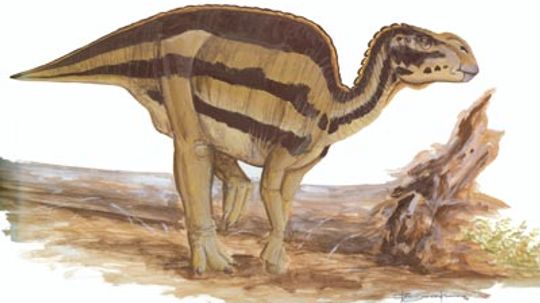
Bactrosaurus ("reptile from Bactria") is known from many skull and skeletal pieces, but not a complete skeleton. Learn more about the Bactrosaurus and other Late Cretaceous dinosaurs.
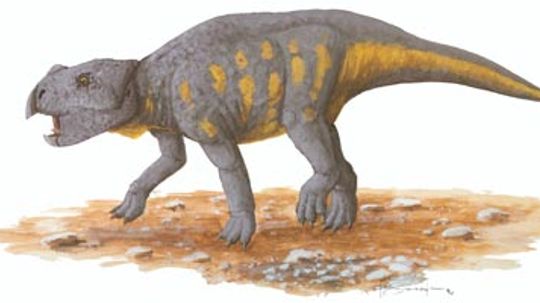
Bagaceratops rozhdestvenskyi was a small protoceratopsian with a big name: "baga" is the Mongolian word for "small," "ceratops" means "horned face," and the species name is in honor of Russian paleontologist A. K. Rozhdestvensky. Learn more about Late Cretaceous dinosaurs.
Brachyceratops montanensis于1913年被发现leontologist Charles W. Gilmore on the Blackfeet Indian Reservation in Montana. Learn more about the Brachyceratops, Late Cretaceous dinosaurs and dinosaurs of all eras.
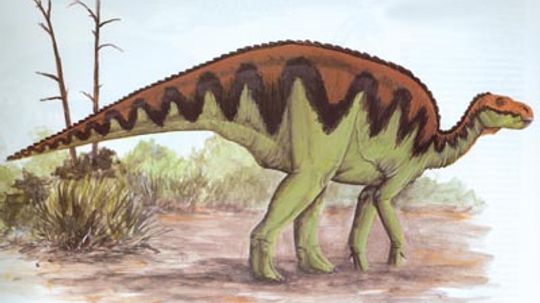
One of the most unusual duckbilled dinosaurs in the Late Cretaceous was Brachylophosaurus ("short-ridged reptile"). This hadrosaurid was discovered and named by Charles Sternberg of Ottawa, Canada, in 1953. Learn more about the Brachylophosaurus.
Advertisement
Centrosaurus, which means "sharp-point reptile," was named by Lawrence Lambe in 1902 from specimens found along the Red Deer River in Alberta. A number of complete skulls and skeletons have since been discovered. Learn more about the Centrosaurus.
Corythosaurus, the "corinthian helmet reptile," was one of the most abundant duckbilled dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous of western North America. Originally found and named by Barnum Brown of the American Museum of Natural History, Corythosaurus is also one of the best known of all dinosaurs.
With its massive head and large teeth, there is no question that Daspletosaurus was master of its world. It got its name because of its ferociousness; its name means "frightful reptile." Learn more about the Daspletosaurus and other Late Cretaceous dinosaurs.
A recently named armored dinosaur, Denversaurus is based on a badly crushed skull from South Dakota. No other parts of the skeleton have been found, so it is difficult to estimate how long or heavy the animal was. Learn more about the Denversaurus.
Advertisement
In 1914, Barnum Brown of the American Museum of Natural History collected a nine-inch-long skull and some foot bones from the Judith River Formation in Alberta. It was named Dromaeosaurus, which means "running reptile." Learn more about the Dromaeosaurus.
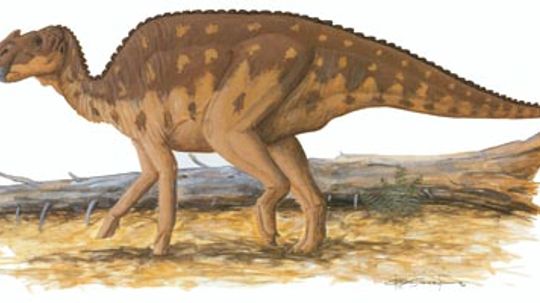
Dromiceiomimus ("emu mimic") has been found both in the Late Cretaceous Horseshoe Canyon and the Judith River Formation of Alberta. It is very similar to Struthiomimus and Ornithomimus, but had much larger eyes and longer, more slender arms. Learn more about the Dromiceiomimus.