Diesel engines are used in many types of vehicles, including locomotives. Diesel engines have a fuel efficiency20 percent greaterthermally than a gas engine. This means a 20 percent increase in fuel economy and therefore lower operating costs than those of a gas engine. Diesel engines also last longer than gas engines because they run at a much slower rpm (revolutions per minute) rate than gas engines do.
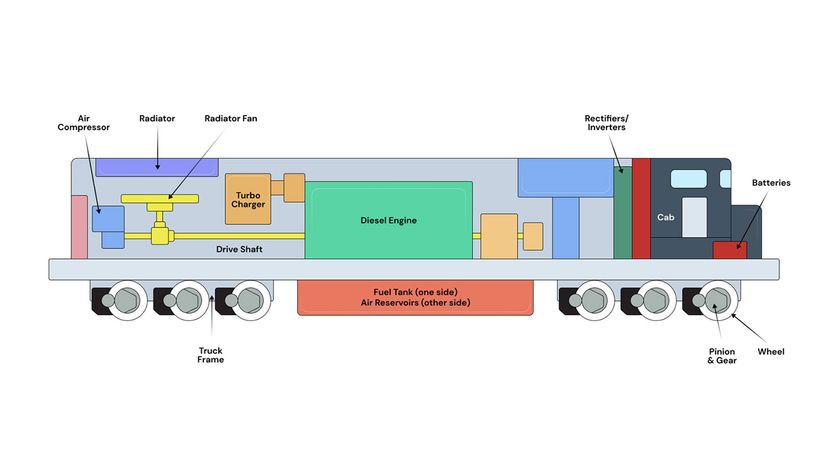
The hybrid diesel locomotive is an incredible display of power and ingenuity. It combines some great mechanical technology, including a huge, 12- to 16-cylinder, two-stroke diesel engine, with some heavy-dutyelectric motorsand generators, throwing in a little bit of computer technology for good measure.
Advertisement
The locomotives weigh between100 and 200 tons(91,000 and 181,000 kilograms) and are designed to tow passenger-train cars at speeds of up to125 miles per hour(200 kph). Siemens' modern engines produce up to 4,200 horsepower, and the generator can turn this into almost4,700 amps of electrical current. The drive motors use this electricity to generate around 60,000 lb-ft of torque. There is also a secondary diesel engine and generator to provide electrical power for the rest of the train. This generator is called thehead-end power unit,生产500至700千瓦(千瓦)electrical power.
This combination of diesel engine and electric generators and motors makes the locomotive ahybrid vehicle. In this article, we'll start by learning why locomotives are built this way and why they have steel wheels. Then we'll look at the layout and key components.
Advertisement