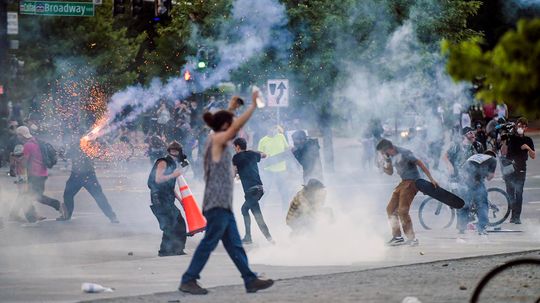Infectious Diseases
Bird flu, malaria, plague and West Nile virus are infectious diseases we've all heard of. Find information on these epidemics and more in this section.

Alpha-gal Syndrome: The Meat Allergy Caused by a Tick
Get Ready for Longer, More Intense Pollen Seasons

Can Pollen Allergies Make You Tired?

People With Asthma, Hay Fever May Have Higher Risk of Psychiatric Disorders

First New Asthma Pill in 20 Years Could Replace Inhalers

Allergy-Asthma Connection

Can you get arthritis from cracking your knuckles?

Who can help treat my arthritis?

What does arthritis do to my joints?

Do You Need to Have a Positive Attitude to Beat Cancer?

8 Thoughtful Ways to Help a Loved One Going Through Chemo

What's the Difference Between a Neoplasm and a Tumor?
What's the Difference Between Cardiac Arrest and a Heart Attack?

How the Graphene Blood Pressure Tattoo Will Change Monitoring

Cyanosis: Why Your Fingers Turn Blue
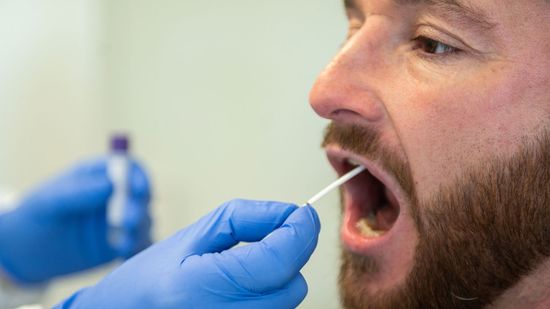
How Can I Tell Whether I Have Flu or COVID-19?
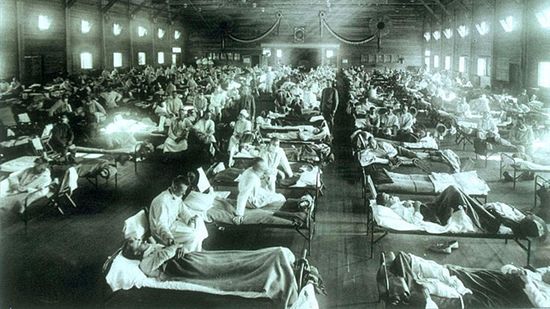
The 1918 Spanish Flu Killed Millions — and Experts Fear It Could Happen Again

Can the Change in Temperature Really Make You Sick?

First Migraine-specific Drugs Show Promise in Studies

10 Tips for How to Relieve Sinus Pressure

4 Occupations Prone to Sinus Trouble
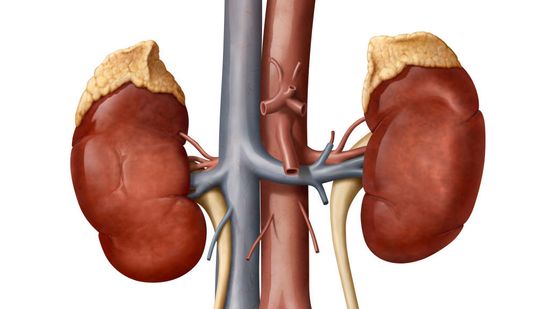
How Many People Could Use the Same Kidney?

Why Diabulimia Is So Dangerous
Turns Out Type 2 Diabetes Is Reversible, After All

New Study: Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Affects Teens More Than Thought

The Mauve Factor

Yeast Overgrowth
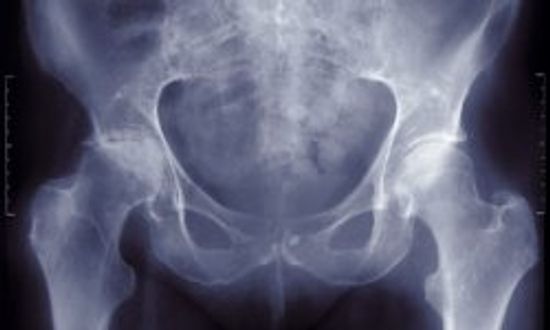
Osteoporosis Diagnosis and Risk Factors

Osteoporosis Questions and Answers

Osteoporosis Treatment

How to Cure A UTI Naturally

Bladder Infections

Interstitial Cystitis

What Is a Low FODMAP Diet and Who Should Try It?

The Curse of Brewing Beer in Your Own Belly

Is the BRAT Diet Still Beneficial?

Why Your Baby Could Be Giving You Mommy Thumb
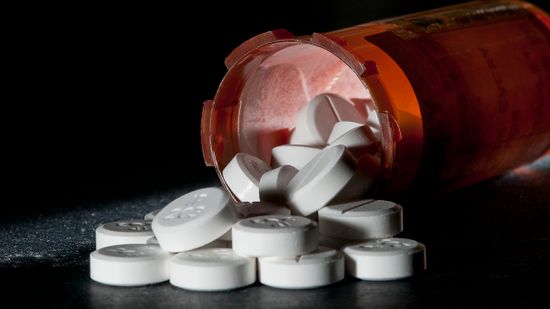
More Than a Third of U.S. Adults Take Prescription Opioids, Millions Misuse Them

How Whole-Body Cryotherapy Works

No Joke: Dead Butt Syndrome Is a Real Pain
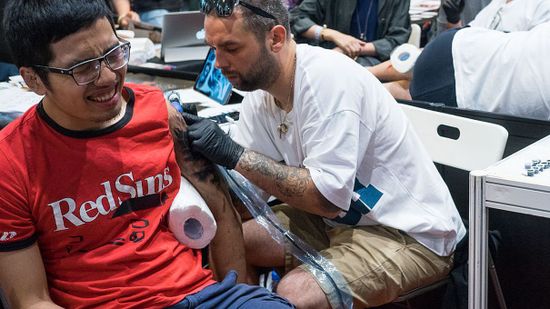
Being a Tattoo Artist Is a Pain in the Neck — Literally

Daily Coffee May Lower Risk of Both Liver Disease and Multiple Sclerosis
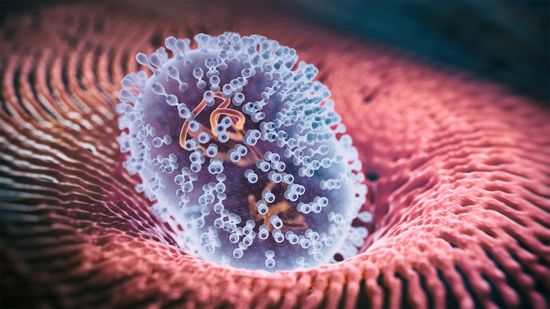
Monkeypox Is a Global Health Emergency, But Don't Panic Yet
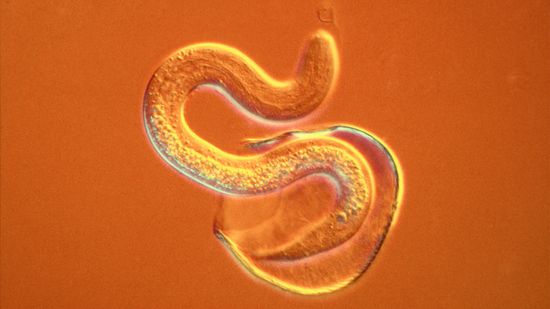
Nematodes: Do We Still Need to Worry About Roundworms and Bare Feet?

坏血病:The Scourge of the High Seas Remains at Large Today

T-cells Are Superheroes in the Battle Against Omicron

20 Years Later, 9/11 Survivors Are Still Experiencing Fallout from Toxic Dust

Masks Are Back and 'War on COVID-19 Has Changed,' CDC Says

Do People Really Die of Old Age?

The Sarco Suicide Pod: Controversial or Compassionate?

Telling Doctors Not to Resuscitate, by Tattoo
Learn More
Is polio making a comeback in the United States and, if so, are you at risk? We talk to a doctor, who says that vaccination is key.
Viruses can alter a person's body odor to make it more attractive to mosquitoes, leading to more bites, which, in turn, allow a virus to spread.
What is the new COVID-19 variant BA.2, and will it cause another wave of infections in the U.S.? Two immunologists from the University of South Carolina weigh in.
Advertisement
Because it has far more mutations than the delta variant does, the new omicron variant may be much more contagious. An expert on emerging viruses explains.
Who gets long COVID and why still remains a mystery, but several new studies are showing it's much more widespread than we initially thought. So what is long COVID and how can it be treated?
We hear many reports of people vaccinated against COVID-19 getting the disease. How does that happen — and why should that not stop us from getting the vaccine?
The wildly contagious delta coronavirus variant now accounts for more than 80 percent of cases in the United States. Does it pose a threat to eliminating COVID-19 across the globe?
Advertisement
How worried should you be about coronavirus variants? A virologist explains why we should pay attention to these five variants, some of which might be new to you.
这是一年世界卫生Organizati新利国际网站品牌官网on officially declared the novel coronavirus a global pandemic. The last 12 months have been truly historic and life-changing in ways that we may not even yet recognize.
Sometimes you just can't avoid using a public bathroom. Is it safe with coronavirus raging? How can you be sure?
Many health experts are gravely concerned about how the massive protest crowds, chanting and especially use of tear gas could accelerate the spread of coronavirus.
Advertisement
Learn the steps of contact tracing, one critical way that public health officials stop viruses like COVID-19 from spreading, in this HowStuffWorks video.
Despite strict closing and mask orders, San Francisco was hit hard by the 1918-1919 influenza pandemic. But some residents balked at the rules and that meant more people died.
As COVID-19 rages around the world, distilleries quickly ramp up the switch from booze to hand sanitizer in an all-out effort to curb the spread.
By杰里米玻璃
The World Health Organization just declared the coronavirus a full-blown pandemic. What does that even mean, and how is that different from an epidemic?
Advertisement
You've probably heard the word "quarantine" a lot in relation to the coronavirus. But how is it different from patient isolation?
There's been a steady uptick in Lyme disease across the United States since 1997, but the news isn't all bad.
Since 2004, cases of diseases spread by ticks and mosquitoes have tripled in the U.S.
We often lack the resources to treat and educate everyone when combating disease. Moving the 'hubs' of a social network to the front of the line may be most effective.
Advertisement
And that unique ability may propel us closer to an HIV vaccine for humans.
Mosquitoes spread deadly malaria, and trimming one specific shrub could make significant headway in battling the disease.
Updated quarantine regulations which would give federal health officials more leeway to detain sick people have some legal and civil rights experts concerned.
Sure, the carrier mosquitoes are in the U.S., and so is the disease. But other factors will stave off a widespread incident, experts say.
Advertisement
Sometimes the nose knows. What advances are being made in detecting diseases by scent?
The FDA is recommending that all blood donations start being tested for Zika virus in the next 12 weeks. But what about the blood already on hand? What happens to that?