Medications
There are medications for just about anything, whether it's a headache or something more serious. Get informed about prescription and over-the-counter drugs and medicine.

Is Your Hospital Diverting Ambulances Because of COVID-19?

How Ambulances Work

Despite Common Myth, Ambulance Companies Can't Avoid Certain Neighborhoods
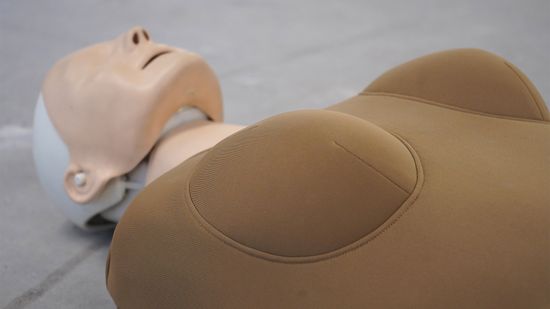
Womanikin: Overcoming the Stigma of Breasts and CPR

Women Less Likely to Receive CPR in Public, Study Finds

Should You Pee on a Jellyfish Sting?
马克博士古巴想解决美国处方ug Price Crisis

World AIDS Day: Lessons of the Past Can Help Safeguard the Future

Epidemiologists Are the 'Disease Detectives' Protecting Public Health

Medical Schools Have Come a Long Way From Grave Robbing to Get Cadavers

Compression Wear Is Key to Sports and Surgical Recovery

Hearing Aids Are About to Get Much More Affordable
Anesthesia Awareness: When You're 'Awake and Aware' During Surgery

Prehab Could Make Your Recovery From Surgery a Bit Easier
Placebo Surgeries Are Effective, But Are They Ethical?

Honey Can Help If Your Child Swallows a Button Battery

What Is the Rarest Personality Type?
Veins, Needles, Yikes: What to Know Before Having Blood Drawn
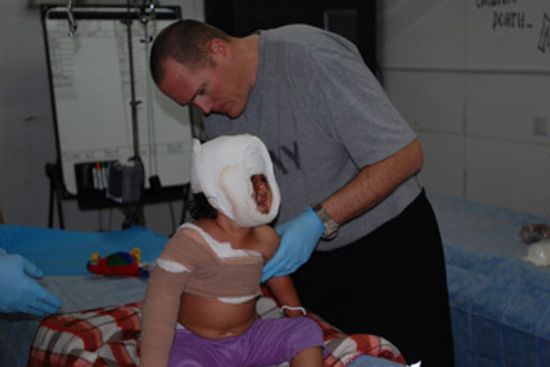
Are Army medics and doctors on the front lines?
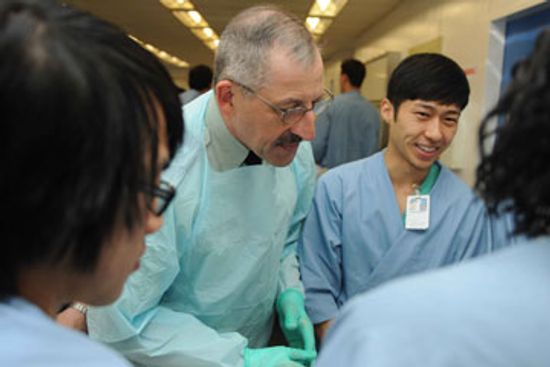
Can civilians become doctors in the U.S. Army?

Do Army doctors and medics carry weapons?
Learn More
Demand for potassium iodide pills has surged since Russia attacked Ukraine and threats of nuclear war loom. But why these pills, and what do they have to do with nuclear radiation?
It all comes down to the type of medicine, how much is required, and how quickly it needs to be absorbed.
吹捧为针对破坏细胞斑块在the brains of Alzheimer's patients, but at $56,000 a year, is Aduhelm a miracle drug or a very expensive experiment?
Advertisement
As both human and animal bodies age, the cushioning connective tissue known as cartilage begins to wear down. That's where glucosamine comes in.
U.S. President Donald Trump has been touting the malaria drug chloroquine as a possible miracle drug for coronavirus. Should we all be taking chloroquine?
If you've got a pain in your head or body, you'll probably reach for whatever's in your medicine cabinet. But is it really the right treatment? One size doesn't fit all – we explain the differences in pain relievers.
When you feel like you're between a rock and a hard place, a stool softener could get you out of a jam.
Advertisement
We're all familiar with the lists of active ingredients on the products we use, but what are inactive ingredients and how can they affect you?
New research from the American of Pediatrics suggests an alarming number of parents are sharing antibiotics that were originally prescribed for their children — and this is bad news for all of us.
Conventional wisdom has long dictated that older people should take a small dose of aspirin each day for their cardiovascular health. A huge new drug trial disagrees.
Chemotherapy was an accidental discovery from World War II. But is it any different in the 21st century?
Advertisement
Have a medicine cabinet full of expired prescriptions? This weekend is the time to get rid of them.
Not all drugs are created equal. And not all drugs are prescribed for the particular conditions they're technically approved to treat, either. That's when they fall into the off-label category, and they're more common than you think.
Hearing loss due to loud noise or certain medicines is irreversible, but soon we might be able to prevent hearing loss before it begins.
Two new studies show that regular use of ibuprofen might lower men's fertility, and even that of a woman's unborn daughter.
Advertisement
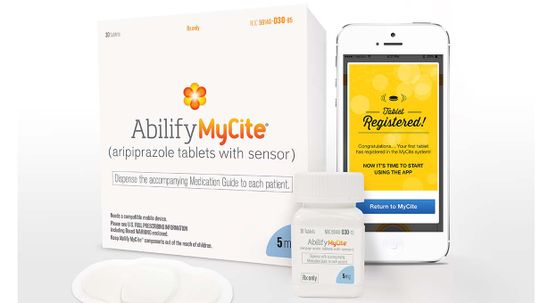
The FDA has approved the first drug for use in the U.S. that includes a digital ingestion tracking system.
A single vial of snakebite antivenom can run thousands of dollars. Why? It actually has little to do with the production process.
A new study found gifts from pharmaceutical reps could be influencing the prescribing behavior of doctors.
In a highly unusual move, Mylan is knocking off its own EpiPen with a cheaper, generic version of the device. It's not the first time a company has done this.
Advertisement
The current U.S. recommendation is to get a tetanus shot every 10 years. Will this new study change CDC guidelines?
It used to an apple that kept doctors away, but researchers have found a Streptococcus strain we could recruit to fight for us against its cavity-causing cousin.
Bee stings hurt, so it seems like an odd proposition to get them on purpose. Believe it or not, the venom that makes that sting may also benefit humans in therapy.
Sometimes it's a lot easier to just take that expired cold medicine than run out to the drugstore when you're feeling sick. But are those expired meds even working? Or, worse, are they causing you harm?
Advertisement
There's an assortment of medications on the market to treat depression. But many of them are also effective for managing other health issues.
Doomsday preppers recommend stocking up for the collapse of civilization -- and that includes antibiotics. But if you're getting them without a prescription, you're getting the veterinary kind.