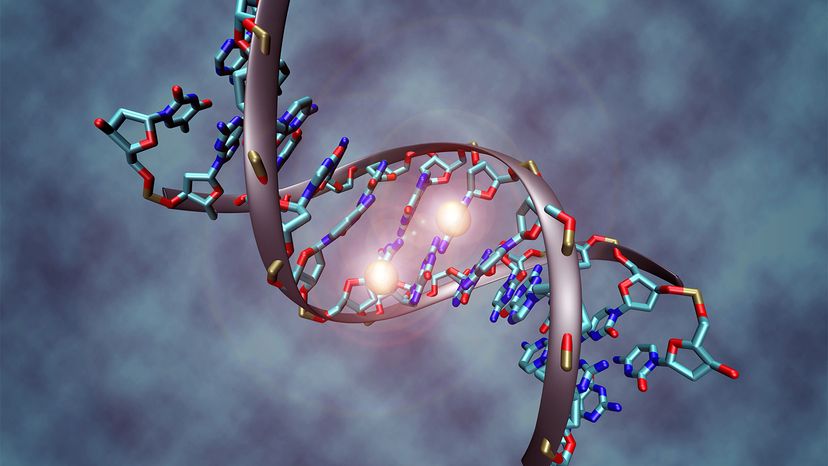
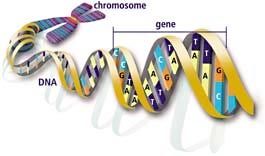
If you guessed that your遗传destiny is based on more than just your DNA, you nailed it. But before we can get to how and why that happens, we should start with some basic definitions. For starters,what the heck is DNA anyway? Those three little letters stand for deoxyribonucleic acid, the master molecule of every cell. DNA contains the essential info that's passed on to every successive generation, and even the slightest change to its sequence (or order) can have serious consequences.
There are four fundamental base types that make up DNA: adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine, (A, C, G and T), and humans have around 3 billion bases, total — believe it or not, over 99 percent of themare identical in all people. Within those billions of bases are about20,000 genes, otherwise known as units of heredity. Some genesprovide instructionsto make molecules called proteins, which carry out life functions, and others don't. Overall though, genes are considered the biological players that influence theregulation and maintenanceof stuff that happens in your body, like the building of bones, the movement of muscles, and the beating of your heart.
All of this makes it sound like your body is permanently set for action from the moment you're born. But that's not the case. One important element we haven't talked about is how the environment or external factors influence the way cells read your genes.
"Epigenetics doesn't actually change the sequence of DNA — that stays the same," Cynthia M. Bulik, Ph.D., FAED, Distinguished Professor of Eating Disorders in the Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, says via email. "But it refers to changes that affect how the genes are read or whether they are expressed or not."
What kinds of changes? All kinds, according to Bulik. "For example, one type of epigenetic change is DNA methylation," she says. "It is when a methyl group gets added to part of a DNA molecule that prevents it from being 'read' and therefore expressed. No protein will be made from that gene because it was basically silenced."